8.1 Our environmental performance
During 2023, our environmental performance has focused, amongst others, on the following activities:
8.2 Impact on climate change
As has been discussed throughout this report, and in particular in Chapter 5.2 Climate adaptation, resilience and transition, at Madrileña Red de Gas we are facing the risks that climate change and the energy transition pose for us, through a commitment and a robust strategy.

Our objectives
At Madrileña Red de Gas, in line with our commitment to the fight against climate change, we have set the following targets for the year 2023:
In relation to these objectives, and in general, at Madrileña Red de Gas we have managed to significantly reduce our electricity consumption, as well as reducing our total waste production by 47%. We have also reduced our Carbon Footprint by 51% and have been able to certify and obtain the Gold Standard seal awarded by OGMP 2.0.
Our carbon footprint
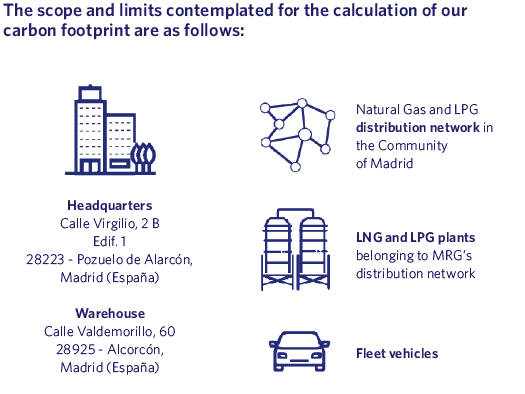
Once again, during 2023 we calculated the carbon footprint associated with our activities, including direct Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions (Scope 1), indirect GHG emissions from the generation of electricity purchased and consumed (Scope 2), as well as indirect emissions occurring in the value chain (Scope 3).
For this calculation we have taken into consideration the following benchmarks:
- Specifications of the standard ISO 14064-1:2019.
- GHG Protocol.
- Methodology EMEP/EEA and IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories.
- Supporting documents prepared for the Registry of carbon footprint, offsetting and absorption projects, created by “Royal Decree 163/2014, of 14 March, which creates the registry of carbon footprint, offsetting and carbon dioxide absorption projects”.
- Internal company procedures.
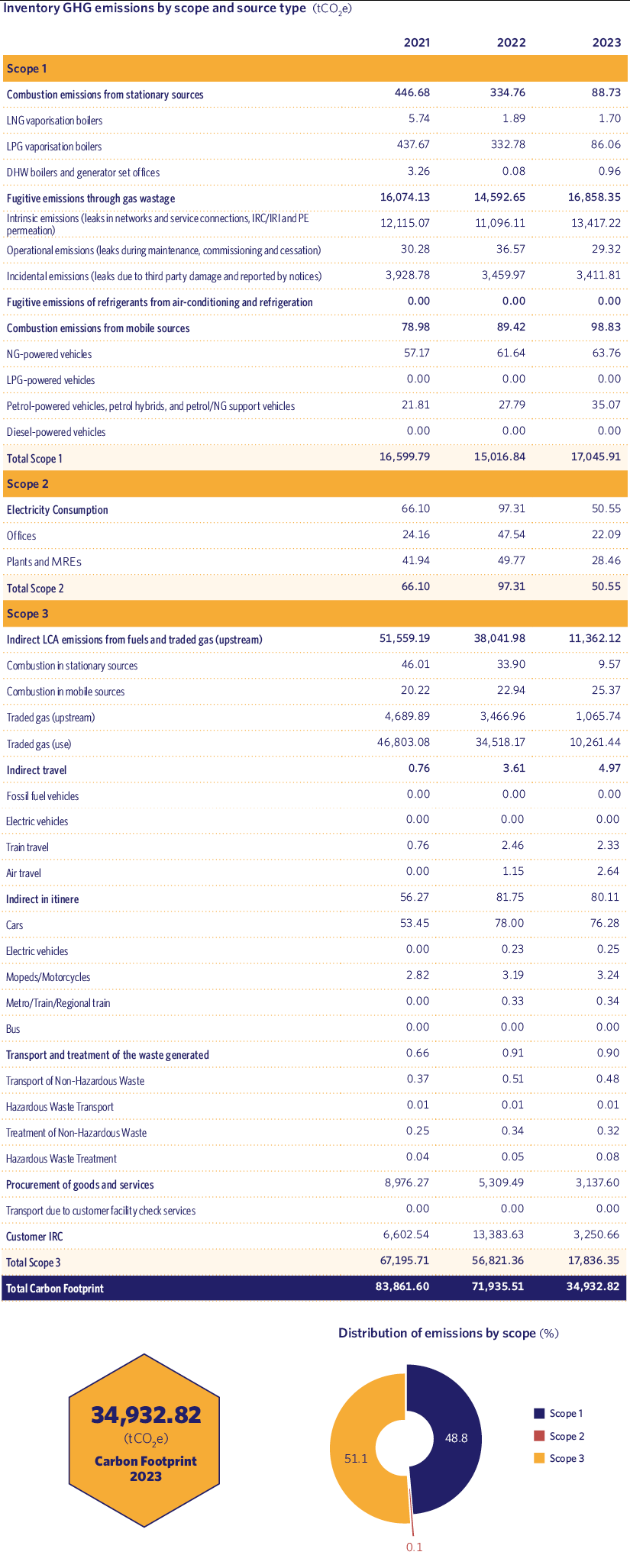
The GHGs included in the HC are CO2, CH4, N2O, SF6, NF3, HFCs and PFCs. All results are reported in CO2e, applying the Warming Potentials given in the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report.
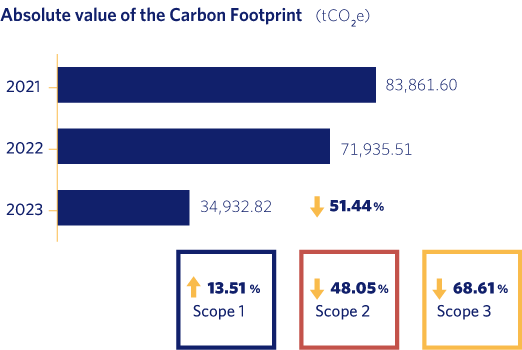
As we can see from the above data, during 2023 we have managed to reduce our carbon footprint by 51.44% compared to the previous year.
Scope 2, relating to our electricity consumption, has been reduced by 48.05% compared to 2022 for the following reasons:
- We have proportionally redistributed the electricity consumption of our headquarters between the two companies that occupy it.
- We have decommissioned most of the LPG storage plants with boilers that need electricity to operate.
With regard to Scope 3 emissions, these have decreased by 68.61% compared to 2022 for several reasons:
- During the year 2023, the number of LPG supply points decreased by 47.93% as they were converted to natural gas, with a consequent reduction of distributed energy corresponding to LPG.
- Methane emissions due to natural gas leaks identified at customer sites have decreased by 75.62%.
Comparison with base year
Not applicable, as this is the second year of the calculation.
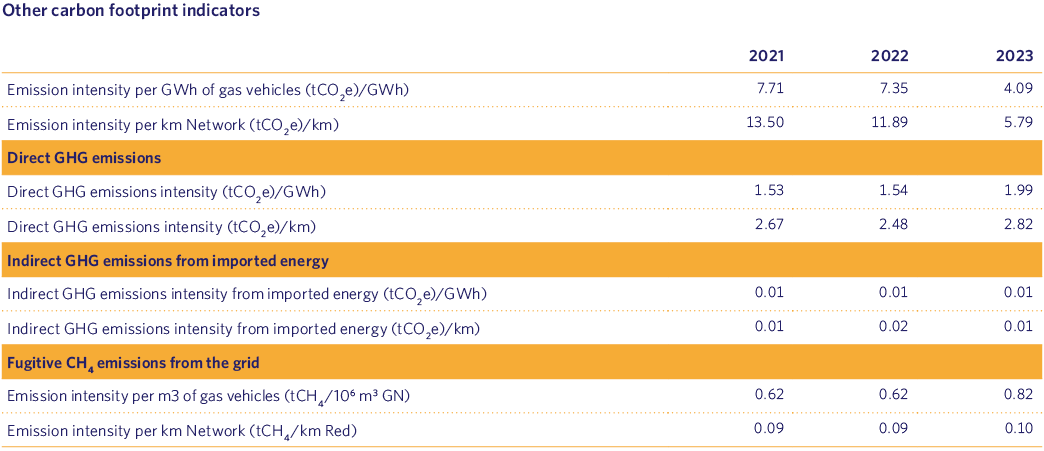
As the base year corresponds to the sum of the emissions of the years 2021 and 2022, analysis of the evolution of the full carbon footprint with respect to the base year will be carried out when two consecutive two-year series are completed, so that comparable results are obtained.
Finally, we would like to note that, with regard to the results of the calculation of our carbon footprint for the previous year, we once again registered it with the Spanish Office for Climate Change (OECC), obtaining the CALCULO seal referring to 2022, in turn registering the corresponding reduction plan.
Other air pollutants
Below, we show the emissions of atmospheric pollutants from both stationary combustion stations and our fleet of vehicles.
For the calculation of emissions in stationary sources, we apply the EMEP/EEA (EMEP/EEA Air Pollutant Emission Inventory Guidebook) methodology, calculating emissions based on fuel consumption and emission factors for the different pollutants, both of which depend on the technology used.
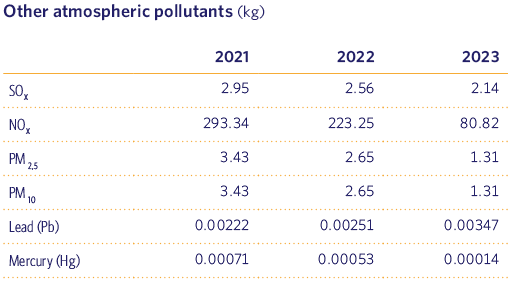
On the other hand, the methodology used to calculate combustion emissions in mobile sources is based on that set out in the Technical Report of the European Environment Agency: COPERT IV (Computer Program to Calculate Emissions from Road Transport), based on the application of emission factors for the different pollutants classified by vehicle type, category (Euro standards) and fuel used.
8.3 Resources and the circular economy
Madrileña Red de Gas is committed to making the most of its resources and trying to give a new life to the waste we generate, in line with the 7 R’s of the Circular Economy:
Resources
Within the framework of our Integrated Environmental Management System, Madrileña Red de Gas has an established system for controlling and monitoring the consumption of resources, with the aim of guaranteeing their adequate management in our work centres and industrial facilities (natural and energy resources) and in the vehicles of our fleet (fuel consumption).
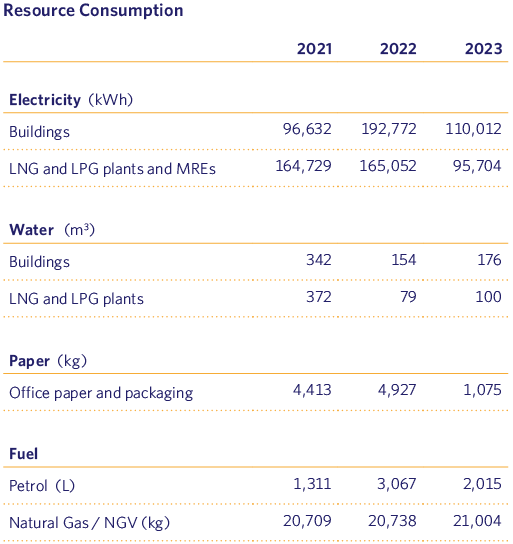
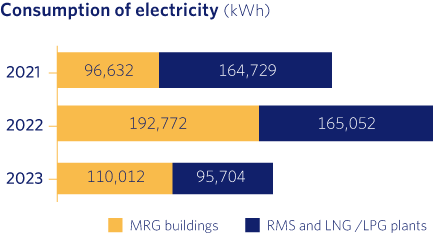
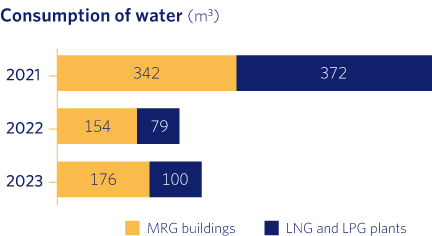
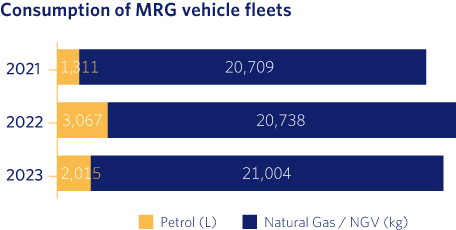
As can be seen from the above results, while the water and fuel consumption of our fleet has remained similar to the previous year, the electricity consumption of our buildings and facilities, as well as our paper consumption, has decreased significantly.
Regarding the decrease in electricity consumption, as mentioned above in the carbon footprint section, as expected, as the number of LPG plants belonging to our company decreases, the consumption associated with them also decreases. Moreover, with regard to paper consumption, every year we make more progress in the digitalisation of our processes, which translates into a considerable reduction in the amount of paper consumed.
Waste Management
To guarantee compliance with this commitment to the circular economy, and within the framework of our Integrated Environmental Management System, we have specific procedures for the correct management of waste.
Thus, whenever possible, actions are carried out with a focus on:
- Applying techniques and alternatives that prevent waste generation.
- Reduction of the amount of waste generated at source.
- Internal or external recovery of waste (reuse or recycling).
The temporary storage of waste in our facilities is carried out in a controlled manner, especially waste that may constitute a degradation hazard for the environment.
In addition, as a general philosophy, we try to ensure that those activities carried out by our contractors contemplate the management of all waste generated during provision of the service in order to ensure maximum simplification of management. To this end, we include appropriate contractual clauses in contracts, and we require our suppliers to be legally authorised to do so.
With regard to the main waste that may be generated at our facilities (regulating and metering stations, LNG and LPG plants), this is mainly due to maintenance operations, e.g. grease, contaminated rags, used filters etc.
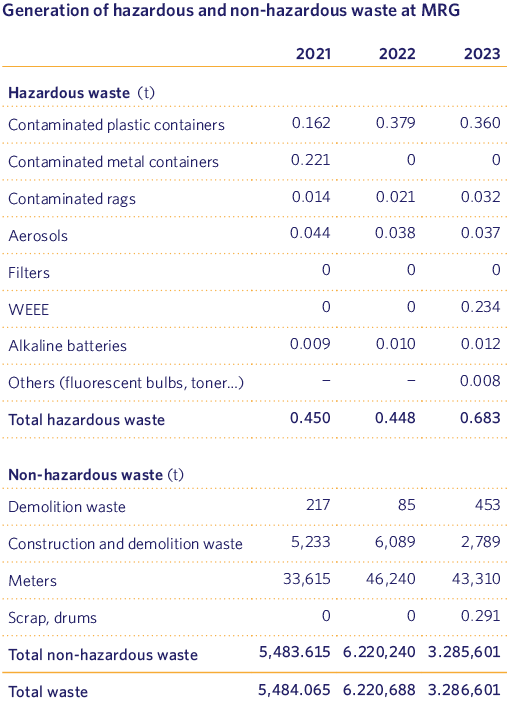
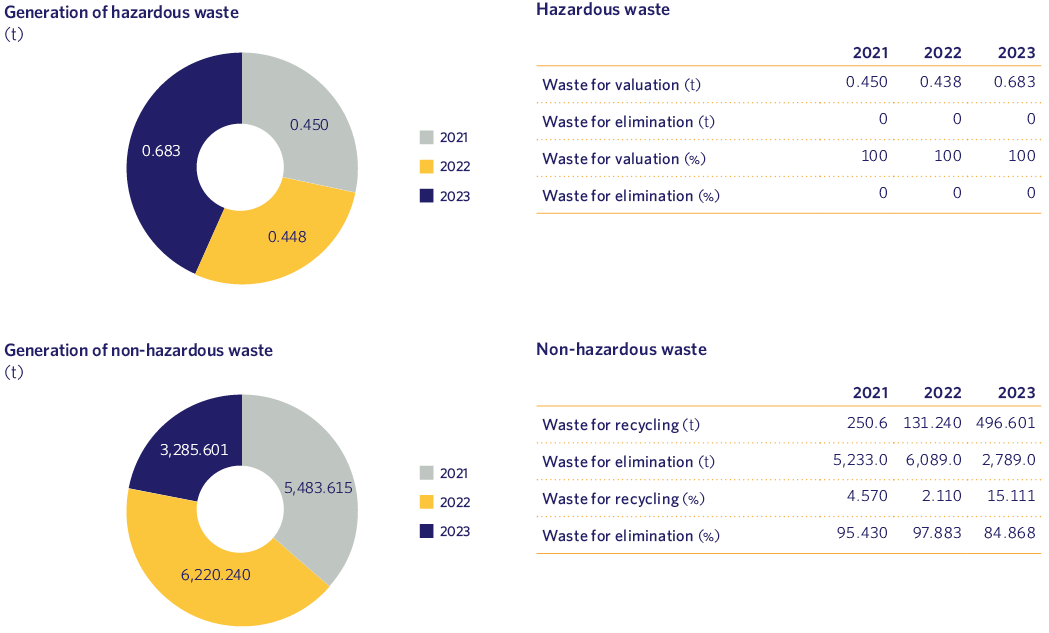
As can be seen from the data, the generation of Hazardous Waste increased during 2023 mainly due to the collection of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) that we have been generating in recent years.
With regard to Non-Hazardous waste, during 2023 we dismantled a total of 37 LPG plants (63 tanks), 23 more than in the previous year, with the consequent generation of waste derived from this activity. It is worth mentioning that, during 2023, we have produced, and registered for the first time on the website of the Autonomous Community of Madrid, the Annual Report of Hazardous Waste Producer, as established by Law 7/2022 on waste and contaminated soils for a circular economy.
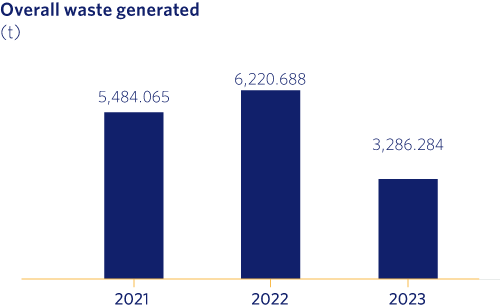
With regard to the overall total of waste generated, as we can see, we have produced 47% less waste compared to the previous year, mainly due to the sharp decrease in the generation of Construction and Demolition Waste as a result of a lower number of works in the expansion activity.
Biodiversity
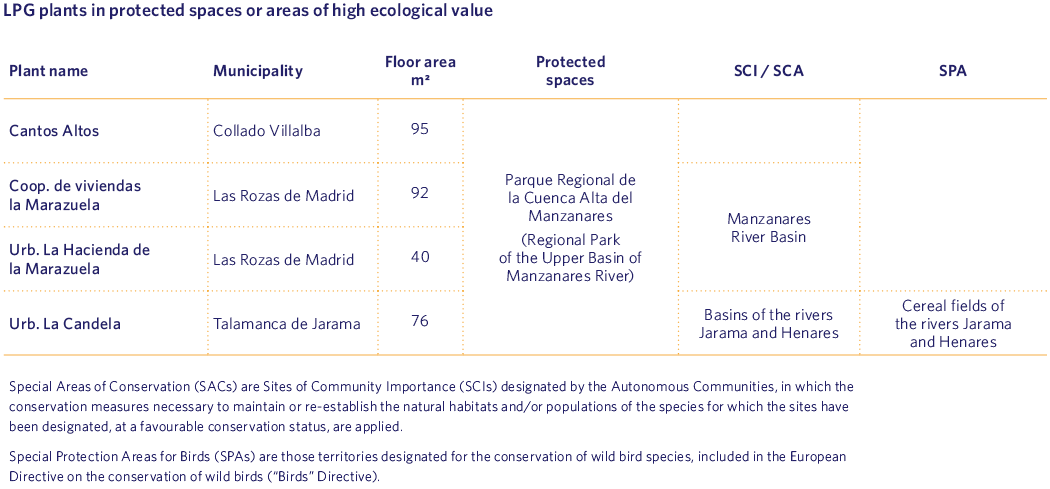
Madrileña Red de Gas is fully aware of the risks involved in the loss of biodiversity, such as the reduction and disappearance of species or the degradation of ecosystems. However, the presence of our facilities in protected areas or areas of high ecological value is very limited, as they are generally urban facilities.
By 2023 we had reduced the number of LPG installations located in protected areas or areas of high ecological value by 71%, amounting to a total of 1398 m2 of reclaimed area.
We currently have 92 LPG satellite plants and five LNG plants that supply gas to homes where the distribution network does not reach. Of these, by the end of 2023, four LPG plants are located in protected areas or areas of high ecological value (none in the case of LNG).
If we compare the number of installations in special areas of conservation with the previous year, the number has decreased considerably. This is because, during 2023, we decommissioned 10 of the plants located on these sites.
By 2023 we had reduced the number of LPG installations located in protected areas or areas of high ecological value by 71%, amounting to a total of 1398 m2 of reclaimed area.
All dismantling activities have a Project Manager, who is responsible for approving the construction- and demolition-waste management plan developed by the contractor at the start of the works and for signing the final works certificate.
In turn, at Madrileña Red de Gas we take data and, where appropriate, samples for drafting of the mandatory Contaminated Soil Closure Report. These reports are submitted to the Competent Authority of the Community of Madrid, which issues an administrative resolution on the matter.
On the other hand, and in relation to possible environmental damage associated with our facilities, we are subject to the obligations established in the Environmental Liability Law (Law 26/2007), among which are the communication of the existence of environmental damage or the imminent threat of such damage to the competent authority, as well as the adoption of measures for prevention, avoidance and repair.
